Supervisor of Master's Candidates
Interfacial deterioration of epoxy-bonded system
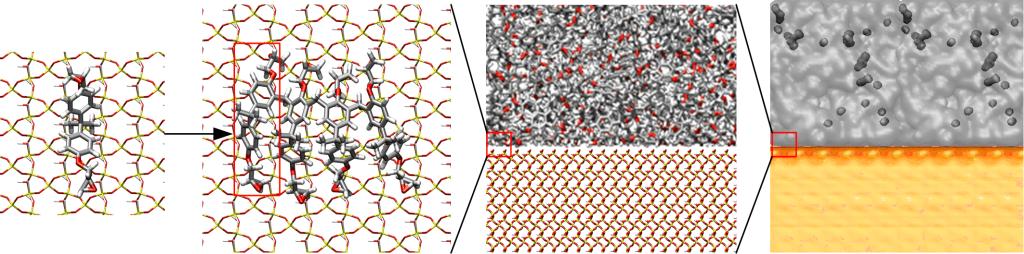
Epoxy bonded to the inorganic substrate can be readily found in micro-electro-mechanical systems. The durability of such material systems is mainly determined by the integrity of bonded interface. Under environmental exposure, the cross-link in epoxy structure can break and moisture can be absorbed into the bonded system. Using molecular dynamics simulation, our research has shown that the epoxy cross-link degrees and water molecules affect the hierarchical structure and molecular interaction of bonded system, which facilitates the epoxy detachment and final interfacial debonding. We have uncovered the relationship between the adhesion of bonded system and the epoxy structure as well as the surrounding environment (i.e. the moisture), and provided the fundamental understanding of the interfacial degradation. The established molecular modeling framework can be applied to predicting the long-term performance of epoxy-bonded system under environmental exposure.
Interfacial deterioration of FRP-wood composite
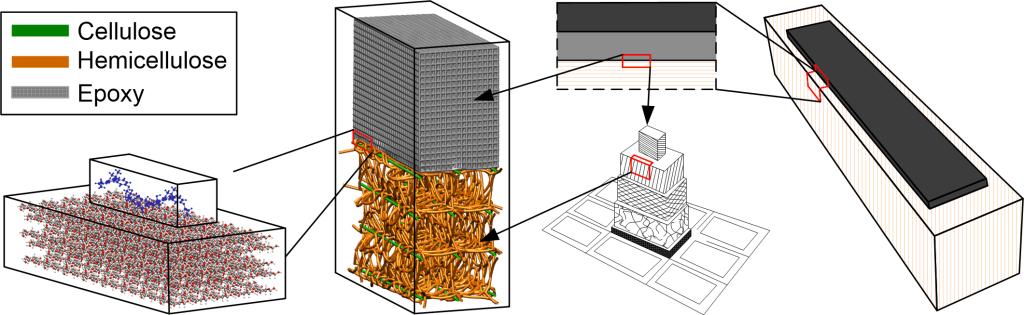
Due to the outstanding properties, FRP composite offers great promise for strengthening the deteriorated infrastructures, including those made of structural wood materials. The durability issue is a major concern for such multilayer composite system, which is mainly associated with the interfacial integrity between epoxy and wood, especially under the exposure to high moisture and temperature levels. To address this issue, we have developed a multiscale modeling approach to construct the atomistic and coarse-grained model of epoxy-wood interface, and characterize the interfacial behaviors under environmental exposures. This works uncovers the degradation mechanism of FRP-wood composite under the exposure to high moisture and temperature levels, which should be carefully considered during the intended service-life.